Recently, XJTU News released a report entitled "BEBC made important progress in the field of cell mechanics microenvironment construction". A research paper, Magnetically Actuated Cell-Laden Microscale Hydrogels for Probing Strain-Induced Cell Responses in Three Dimensions, was published on a journal of Nature Publishing, NPG Asia Materials (IF 10.118), by BEBC. This work was accomplished by a doctoral candidate Yuhui Li under the supervision of Prof. Feng Xu and Dr. Guoyou Huang.
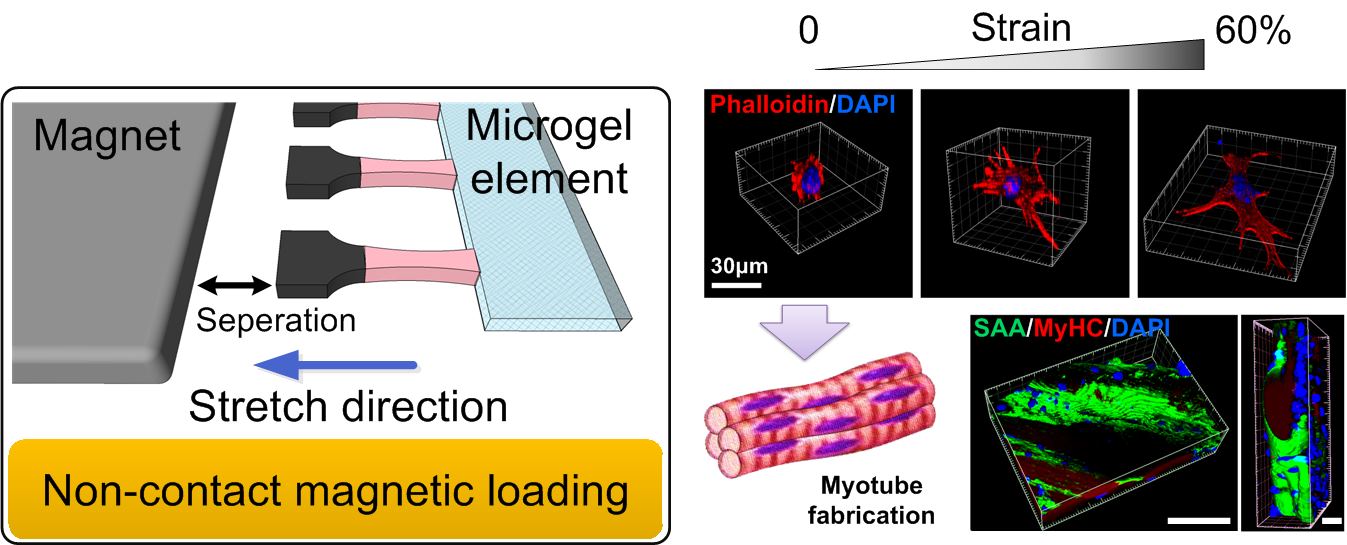
Abstract: Living cell respond to their mechanical microenvironments during development, healing, tissue remodeling and homeostasis attainment. However, this mechanosensitivity has not yet been established definitively for cells in three-dimensional (3D) culture environments, in part because of challenges associated with providing uniform and consistent 3D environments that can deliver a large range of physiological and pathophysiological strains to cells. Here, we report microscale magnetically actuated, cell-laden hydrogels (μMACs) for investigating the strain-induced cell response in 3D cultures. μMACs provide high-throughput arrays of defined 3D cellular microenvironments that undergo reversible, relatively homogeneous deformation following non-contact actuation under external magnetic fields. We present a technique that not only enables the application of these high strains (60%) to cells but also enables simplified microscopy of these specimens under tension. We apply the technique to reveal cellular strain-threshold and saturation behaviors that are substantially different from their 2D analogs, including spreading, proliferation, and differentiation. μMACs offer insights for mechanotransduction and may also provide a view of how cells respond to the extracellular matrix in a 3D manner.
This paper was also selected as Nature Highlight. Congratulations to them! Look forward to more high impact work from BEBC!

XJTU News link: http://news.xjtu.edu.cn/info/1004/61685.htm
Paper link: http://www.nature.com/am/journal/v8/n1/abs/am2015148a.html